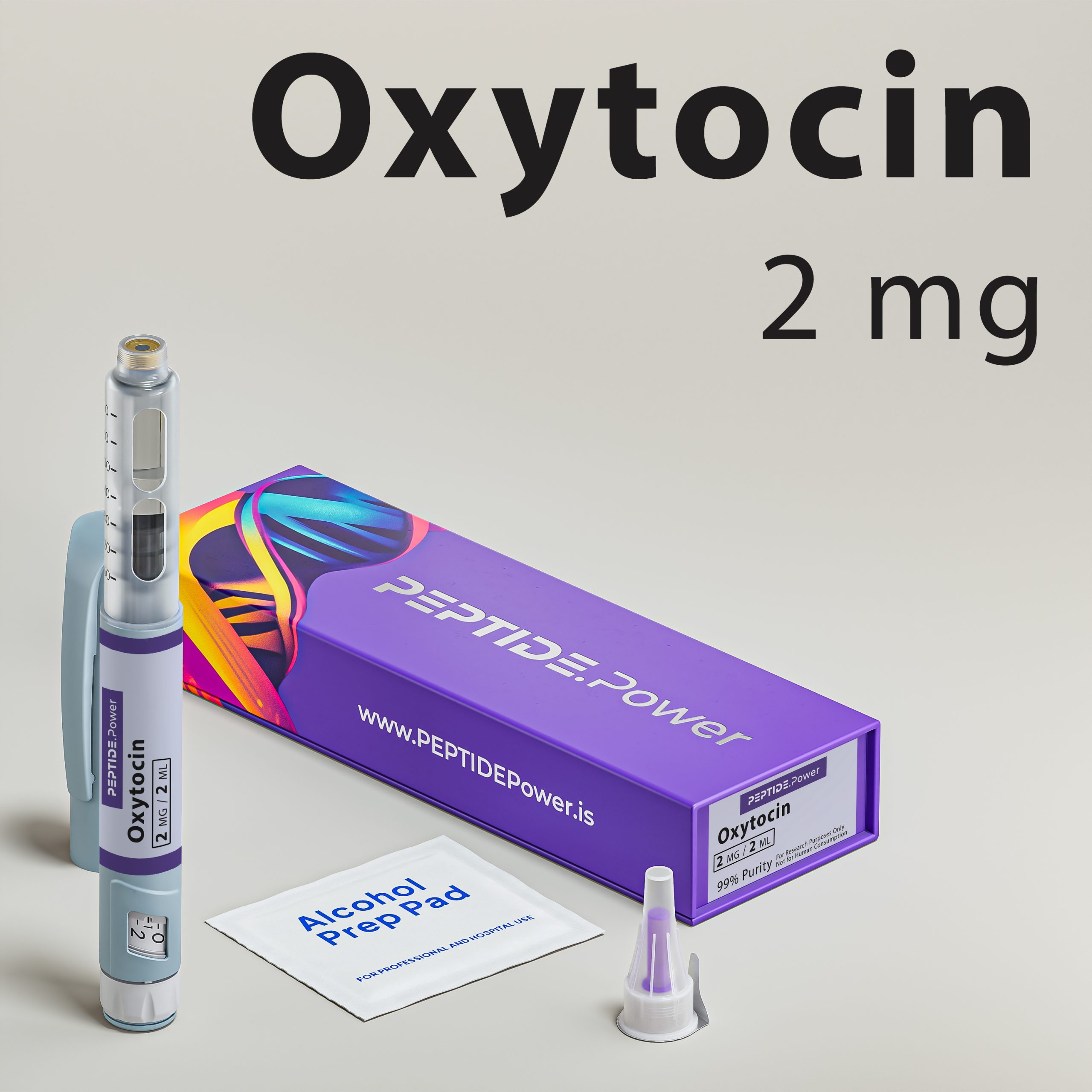
Oxytocin - Connection, Trust & Emotional Regulation
Description
Oxytocin is a nine-amino-acid neuropeptide hormone synthesized in the hypothalamus and released from the posterior pituitary gland. It plays a central role in social behavior, emotional bonding, reproductive physiology, and stress-response modulation. In research settings, oxytocin is studied for its effects on social cognition, attachment behavior, anxiety signaling, and autonomic nervous system balance.
Our formulation is provided in a stabilized pre-mixed injection pen for SubQ administration. Subcutaneous delivery supports controlled systemic exposure and predictable neuroendocrine engagement in experimental protocols. Each unit is freshly prepared to preserve peptide integrity and ensure standardized dosing. The product is intended strictly for laboratory and research use only.
In clinical and laboratory research, oxytocin has been observed to bind oxytocin receptors (OXTR) expressed in limbic brain regions, including the amygdala, hippocampus, and hypothalamus. Receptor activation influences social behavior circuits, stress-related hormone signaling, and autonomic nervous system regulation. Research domains include behavioral neuroscience, attachment biology, stress physiology, and reproductive signaling studies.
Clinical Status
Human RCT ✔ | Observational ✔ | Animal ✔ | In vitro ✔
Extensively studied in human behavioral, neuroendocrine, and reproductive research domains.
Mechanism of Action
Oxytocin binds to oxytocin receptors (OXTR) in the brain and peripheral tissues, influencing neural circuits involved in bonding, emotional regulation, and stress response. Receptor activation modulates activity in the amygdala and hypothalamus, areas central to emotional processing and autonomic control. This interaction affects neurotransmitter systems including dopamine and serotonin pathways, contributing to behavioral and physiological responses observed in research models.
Benefits
- Enhancement of social bonding circuits:
Oxytocin has been extensively studied for its role in modulating neural circuits responsible for attachment and affiliative behavior. It influences activity within the amygdala, nucleus accumbens, and prefrontal cortex, regions central to social recognition and emotional valuation. Functional imaging studies demonstrate altered limbic activation patterns following oxytocin exposure. These changes are associated with increased salience of social cues and enhanced interpretation of facial expressions. Research suggests that oxytocin strengthens neural pathways involved in trust formation and interpersonal bonding. Its role in pair-bond formation models further supports its importance in social neuroscience research. The peptide’s effects appear context-dependent, interacting with baseline emotional state and environmental factors. - Modulation of fear and threat perception pathways:
Oxytocin signaling has been shown to influence amygdala reactivity, particularly in response to perceived social threat stimuli. Experimental studies demonstrate reduced hyperactivation of fear-processing circuits during controlled social stress tasks. This modulation affects how emotional salience is assigned to environmental cues. Neurobiological models suggest that oxytocin alters the balance between excitatory glutamatergic signaling and inhibitory interneuron activity within limbic networks. These effects contribute to a recalibration of threat perception in research settings. Importantly, oxytocin does not eliminate fear responses but may influence their intensity and contextual interpretation. - Interaction with dopaminergic reward circuitry:
Oxytocin interacts with dopaminergic neurons within the mesolimbic pathway, particularly projections between the ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens. This interaction plays a central role in reinforcing social attachment behaviors. Studies indicate that oxytocin may enhance the perceived reward value of social interaction. Neurochemical cross-talk between oxytocin and dopamine systems supports motivation-linked bonding behaviors. These interactions extend beyond simple hormonal signaling and involve coordinated neurotransmitter modulation. This reward integration distinguishes oxytocin from purely peripheral endocrine agents. - Regulation of stress-response neuroendocrine balance:
Oxytocin influences hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity through central hypothalamic signaling. Research demonstrates altered cortisol dynamics following oxytocin administration in controlled environments. The peptide appears to participate in feedback regulation of stress hormone release. Neuroendocrine models suggest modulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone neurons within the paraventricular nucleus. This coordinated signaling may contribute to balanced stress adaptation rather than blunt suppression. Oxytocin’s integration within stress-response circuits supports its inclusion in resilience-focused research domains. - Autonomic nervous system integration:
Oxytocin receptors are expressed in both central autonomic nuclei and peripheral tissues. Experimental data indicate influence on parasympathetic tone and cardiovascular variability markers. Heart rate variability studies suggest enhanced vagal activity under certain research conditions. These autonomic changes highlight the connection between emotional processing and physiological regulation. Oxytocin therefore represents a bridge between central neural circuits and peripheral physiological responses. - Social cognition and emotional inference signaling:
Behavioral experiments demonstrate altered performance in tasks measuring trust, empathy, and recognition of emotional states. Oxytocin appears to influence higher-order cognitive appraisal of social cues. Neuroimaging research shows modulation of connectivity between the amygdala and medial prefrontal cortex. These connectivity changes are associated with shifts in social decision-making patterns. The peptide’s cognitive effects are nuanced and influenced by baseline personality traits and contextual variables. This complexity reinforces its classification as a modulatory neuropeptide rather than a simple stimulant. - Neuroplasticity and synaptic modulation:
Emerging research suggests oxytocin may influence synaptic plasticity within hippocampal and limbic circuits. Modulation of intracellular calcium signaling following receptor activation affects neuronal excitability and synaptic strength. These cellular mechanisms support adaptive learning processes related to social memory. Oxytocin’s involvement in long-term potentiation models has been explored in animal studies. This synaptic dimension extends its relevance beyond acute behavioral modulation into structural neural adaptation research. - Reproductive and attachment biology signaling:
Oxytocin is deeply integrated within reproductive physiology, particularly in maternal bonding and pair-bond formation models. Neural release patterns during childbirth and lactation highlight its evolutionary role in attachment. Experimental research in monogamous species demonstrates strong involvement in partner preference formation. These biological foundations inform its broader study in attachment neuroscience and social behavior research contexts. - Controlled subcutaneous delivery for research protocols:
Provided in a stabilized pre-mixed injection pen for SubQ administration, oxytocin supports predictable systemic exposure in experimental settings. Subcutaneous delivery allows structured dosing parameters and reproducible research conditions. Each unit is freshly prepared and intended strictly for laboratory use only.
Research Data
xxx
Stack Suggestions
xxx
Pen Dosage Chart
Dosage & Protocols Variations
xxx
Possible Side Effects
xxx
Product Attributes
xxx
Scientific References
xxx
Included In The Box
Every product arrives in a premium, custom-designed PEPTIDE.Power box, engineered for convenience, hygiene, and safe storage in your refrigerator. Inside, you will find everything needed for your full research protocol:
- 1× Disposable Pre-Mixed Injection Pen
- Powered by our proprietary PSM Technology™ – precision stabilization & mixing system for consistent potency
- 10× Ultra-thin Needles (33G, 4 mm)
- 10× Alcohol Pads for sterile preparation
- Internal Stabilizing Foam Insert to prevent shaking during transport
- Instruction Panel printed on the inside of the box for quick reference
- Security Seal Sticker ensuring the package has not been opened or tampered with
Storage
Store the product in a refrigerator at 1 – 7°C immediately upon delivery. To maintain optimal stability, keep the pen away from light, and do not expose it to repeated temperature changes.
Once reconstituted (all our pens come pre-mixed), research compounds remain stable for 6 – 8 weeks under proper refrigeration.
Do not freeze after reconstitution. Always keep the box closed so the pen, needles, and alcohol pads stay clean and protected.
For best results, use the product consistently within the recommended time window and always follow your research protocol.
Delivery
We ship with Next-Day EU Delivery via DHL Express or UPS Express.
All orders are prepared fresh on the day of dispatch, placed in EPS cold-chain transport boxes, and shipped with cooling elements to maintain a stable temperature throughout the journey.
Our logistics process is designed so the package arrives overnight, avoiding customs delays inside the European Union.
Products are shipped from our EU facility, ensuring no import duties, no customs clearance, and always fast and secure delivery.
Payment
Due to the nature of research peptides and the high-risk category assigned by payment processors, credit card companies do not support merchants in this field.
For this reason, we accept bank transfers only.
Within the European Union, SEPA transfers are fast, low-cost, and usually arrive within minutes to a few hours, making the payment process smooth and simple.
Once the transfer is received, your order is prepared immediately and dispatched the same day (cut-off dependent).
This method ensures compliance, security, and continuity of service for all customers across the EU.