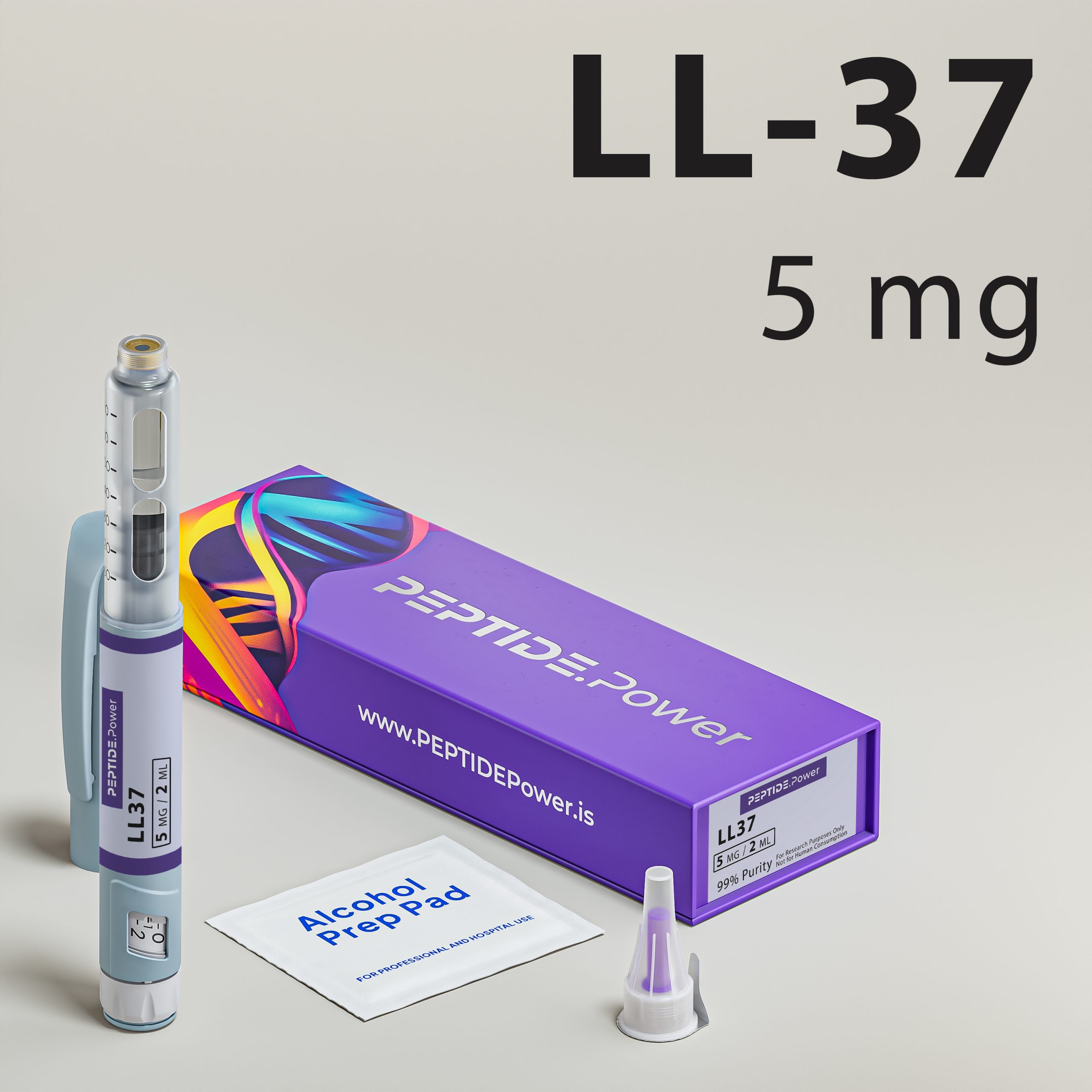
LL-37
$74.40
LL-37 - Antimicrobial & Immune Modulation
Description
LL-37 is the only known human cathelicidin-derived antimicrobial peptide, produced from the precursor protein hCAP-18. It plays a central role in innate immune defense by directly interacting with microbial membranes and modulating immune signaling pathways. LL-37 is expressed in neutrophils, epithelial tissues, and barrier surfaces, contributing to first-line host defense mechanisms.
Our formulation is provided in a stabilized pre-mixed injection pen for SubQ administration. Subcutaneous delivery supports controlled systemic exposure and predictable immune signaling engagement in research protocols. Each unit is freshly prepared to preserve structural integrity and standardized dosing. The product is intended strictly for laboratory and research use only.
In preclinical and translational research, LL-37 has been observed to exhibit antimicrobial activity against bacteria, viruses, and fungi while also influencing cytokine production and chemotactic signaling. It participates in immune cell recruitment, angiogenesis modulation, and wound repair processes. Research domains include host defense biology, barrier function studies, inflammatory regulation, and tissue regeneration investigations.
Clinical Status
Human RCT ▣ | Observational ▣ | Animal ✔ | In vitro ✔
Primarily studied in innate immunity, antimicrobial defense, and inflammatory modulation research contexts, with limited exploratory human data.
Mechanism of Action
LL-37 supports innate immune defense by directly interacting with microbial membranes and modulating host immune signaling pathways. It disrupts pathogen membranes while also influencing cytokine release and immune cell recruitment. This dual antimicrobial and immunomodulatory profile distinguishes LL-37 within host defense research.
Benefits
- Broad-spectrum antimicrobial membrane destabilization:
LL-37 is a cationic amphipathic peptide that preferentially binds negatively charged phospholipids present on microbial membranes. Through electrostatic attraction and hydrophobic insertion, it disrupts membrane integrity and induces structural destabilization. This mechanism results in rapid membrane permeability changes rather than inhibition of intracellular enzymatic pathways. Because its activity is membrane-targeted, it does not rely on specific metabolic targets that commonly mutate in antibiotic resistance models. In vitro systems demonstrate disruption of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial membranes as well as certain viral envelopes. This structural mode of action positions LL-37 as a host-defense peptide rather than a classical antimicrobial compound. - Integration within innate immune signaling networks:
Beyond direct pathogen interaction, LL-37 functions as an immunomodulatory mediator. It interacts with toll-like receptor pathways and modulates downstream NF-kB signaling cascades. This influence alters cytokine and chemokine expression patterns in epithelial and immune cells. LL-37 does not act as a simple immune stimulant but rather fine-tunes inflammatory signaling intensity depending on environmental context. This regulatory capability supports coordinated innate immune activation rather than excessive inflammatory amplification. - Chemotactic recruitment of immune effector cells:
LL-37 participates in chemotactic signaling processes that attract neutrophils, monocytes, dendritic cells, and T lymphocytes to sites of microbial exposure. Experimental models show increased migration of immune cells toward LL-37 concentration gradients. This recruitment facilitates early containment of pathogens before adaptive immunity becomes dominant. Its role in shaping immune cell trafficking dynamics highlights its importance in early-phase host defense biology. - Modulation of epithelial barrier defense mechanisms:
LL-37 is expressed in skin, respiratory epithelium, and gastrointestinal mucosa, where it contributes to surface-level microbial regulation. It influences tight junction integrity and epithelial cell proliferation in laboratory models. These effects support structural barrier resilience against microbial invasion. By integrating antimicrobial action with barrier maintenance, LL-37 serves as a multifunctional component of first-line defense systems. - Angiogenic and tissue repair signaling involvement:
Research indicates that LL-37 influences endothelial cell migration and angiogenic signaling pathways. It has been associated with vascular endothelial growth factor modulation in experimental systems. These effects contribute to organized tissue repair responses following injury. The peptide’s involvement in both immune defense and regenerative processes reflects its dual functional role within host physiology. - Context-dependent regulation of inflammatory cascades:
LL-37 demonstrates the capacity to either enhance or suppress inflammatory mediator expression depending on cellular environment. In certain models, it reduces excessive pro-inflammatory cytokine production, while in others it enhances targeted immune activation. This context-dependent modulation suggests a role in immune calibration rather than linear stimulation. Such flexibility is central to its positioning within immune balance research domains. - Interaction with microbial biofilm dynamics:
Biofilms represent structured microbial communities resistant to conventional antimicrobial therapies. LL-37 has been evaluated for its ability to interfere with biofilm formation and structural integrity in experimental systems. Membrane disruption and interference with microbial communication pathways contribute to this activity. These findings extend its research relevance into antimicrobial resistance and chronic infection models. - Host-pathogen interface signaling integration:
LL-37 operates at the interface between host tissue and microbial exposure. It integrates membrane-level antimicrobial action with intracellular immune signaling modulation. This dual functionality allows coordinated responses involving pathogen clearance, immune recruitment, and tissue remodeling. Its evolutionary conservation within the cathelicidin family underscores its central role in innate host defense biology. - Controlled subcutaneous delivery for structured immune research:
Provided in a stabilized pre-mixed injection pen for SubQ administration, LL-37 supports predictable systemic exposure in experimental protocols. Subcutaneous delivery allows structured dosing parameters and reproducible immune engagement conditions. Each unit is freshly prepared and intended strictly for laboratory use only.
Research Data
xxx
Stack Suggestions
xxx
Pen Dosage Chart
Dosage & Protocols Variations
xxx
Possible Side Effects
xxx
Product Attributes
xxx
Scientific References
xxx
Included In The Box
Every product arrives in a premium, custom-designed PEPTIDE.Power box, engineered for convenience, hygiene, and safe storage in your refrigerator. Inside, you will find everything needed for your full research protocol:
- 1× Disposable Pre-Mixed Injection Pen
- Powered by our proprietary PSM Technology™ – precision stabilization & mixing system for consistent potency
- 10× Ultra-thin Needles (33G, 4 mm)
- 10× Alcohol Pads for sterile preparation
- Internal Stabilizing Foam Insert to prevent shaking during transport
- Instruction Panel printed on the inside of the box for quick reference
- Security Seal Sticker ensuring the package has not been opened or tampered with
Storage
Store the product in a refrigerator at 1 – 7°C immediately upon delivery. To maintain optimal stability, keep the pen away from light, and do not expose it to repeated temperature changes.
Once reconstituted (all our pens come pre-mixed), research compounds remain stable for 6 – 8 weeks under proper refrigeration.
Do not freeze after reconstitution. Always keep the box closed so the pen, needles, and alcohol pads stay clean and protected.
For best results, use the product consistently within the recommended time window and always follow your research protocol.
Delivery
We ship with Next-Day EU Delivery via DHL Express or UPS Express.
All orders are prepared fresh on the day of dispatch, placed in EPS cold-chain transport boxes, and shipped with cooling elements to maintain a stable temperature throughout the journey.
Our logistics process is designed so the package arrives overnight, avoiding customs delays inside the European Union.
Products are shipped from our EU facility, ensuring no import duties, no customs clearance, and always fast and secure delivery.
Payment
Due to the nature of research peptides and the high-risk category assigned by payment processors, credit card companies do not support merchants in this field.
For this reason, we accept bank transfers only.
Within the European Union, SEPA transfers are fast, low-cost, and usually arrive within minutes to a few hours, making the payment process smooth and simple.
Once the transfer is received, your order is prepared immediately and dispatched the same day (cut-off dependent).
This method ensures compliance, security, and continuity of service for all customers across the EU.